Fujitsu has revealed details about its new high performance CPU, destined for the Post-K supercomputer. The A64FX is a Fujitsu designed Arm processor and is of particular note as it is the first to implement the Arm v8-A SVE architecture (SVE = Scalable Vector Extensions). Architectural details of the A64FX were shared at the Hot Chips 30 symposium yesterday evening in Cupertino, California. Fujitsu today emailed HEXUS a press release concerning further Post-K CPU specifications, yet to be shared on its website.
It is claimed that the new A64FX builds upon 60 years' worth of Fujitsu-developed microarchitecture and expertise in previous supercomputers, mainframes, and UNIX servers, and is the first CPU in the world to adopt SVE. "With hardware technology that draws out the high memory bandwidth of high performance stacked memory, the system can efficiently utilize the CPU's high functional computational processing units, enabling delivery of high application execution performance," says Fujitsu.
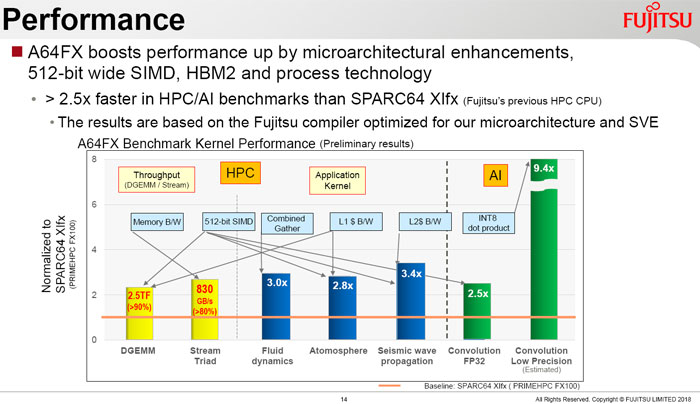
An A64FX chip offers peak double precision (64-bit) floating point performance of over 2.7 TFLOPS and has a computational throughput twice that amount for single precision (32-bit), and four times that amount for half precision (16-bit). It offers high performance, high throughput, plus high efficiency and works with binary standards compatible with Arm v8.2A plus SVE and SBSA (Server Base System Architecture). The chip is eminently suitable for a wide range of processing fields such as big data and AI - as well as traditional supercomputer tasks.
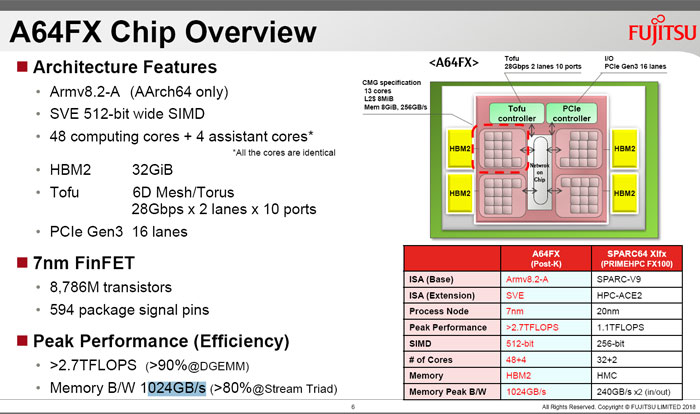
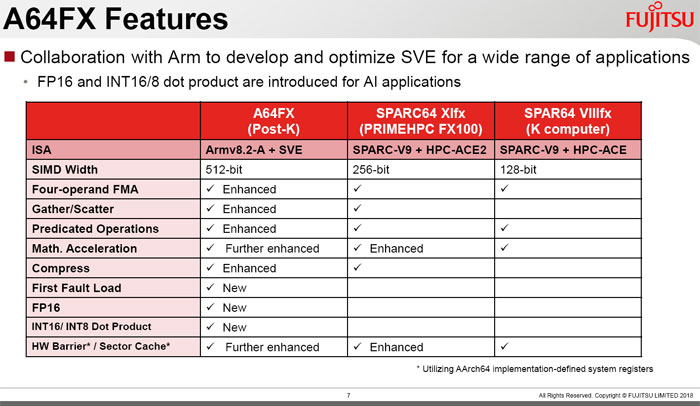
Peeking at the architectural diagram above, you can see the 7nm A64FX contains 48 computing cores plus four assistant cores, with all the cores being identical. Integral to the chip are the 32GiB HBM2, Tofu controller (with 28Gbps, 2 lanes and 10 ports), and PCIe Gen3 controller with 16 lanes. As mentioned previously this many-core chip can deliver over 2.7 TFLOPS, and its memory bandwidth is 1024GB/s. You can compare this to the SPARC64 Xlfx processor, a refined version of the SPRC processor in the original K Computer, in the above diagram, and in features below.
The Post-K Computer is scheduled to be operational by 2021 and is aiming to achieve application execution performance up to 100 times that of the K computer.