Google has updated its Android Security Rewards Program Rules and scope of the program with the juiciest bounties ever. Among the list of prizes now on offer for finding vulnerabilities in Google's Android OS and devices is a $1m reward for an exploit that bypasses the Pixel Titan M security chip. Additionally, any prize can be uplifted by 50 per cent if any security researcher is able to find an exploit via developer preview versions of Android.

Announced in October 2018, the Titan M security chip was claimed to make the Pixel 3 the most secure Google smartphone yet. It looks after the verified boot secure boot process, intelligently verifies your lock screen password entry, provides secure on-device encryption / decryption, secures transactions in third party apps, and is designed to prevent unauthorised tampering of any kind. The Titan M was built into devices starting with the Google Pixel 3 and later - up to the current Pixel 4.
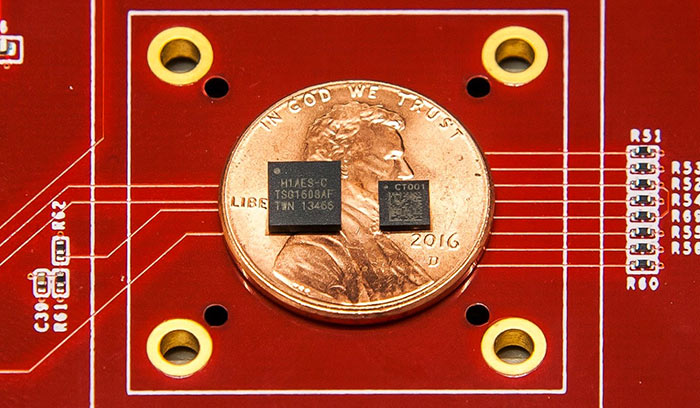
Titan M (right) shown next to its server counterpart.
Google is understandably precious about its Titan M security performance and this is the reason for the potential life-changing bounty available to bug hunters. To qualify for the biggest reward researchers much find an Android "full chain remote code execution exploit with persistence," that also compromises data protected by the Titan M. As mentioned in the intro, if it works on a developer preview of Android, you can get up to $1.5 for your work. Google likes to find exploits in developer previews as it can then plug any holes ahead of the OS going onto millions of real-world shipping devices.

In its report on the updated bounty amounts, ZDNet remarks that no one has ever managed to earn a top reward from developing hacks for the Android Vulnerability Rewards Program (VRP) since it was started in 2015. It reckons that the $1m plus prize announced this week will never be claimed either as remote exploits are hard to create due to the limited attack surface. Then the added 'persistence' qualifier puts the top prize even further out of reach.
Google told ZDNet that it had seen just two complete full chain Remote Code Execution exploits since the program began. Both were discovered by researcher Guang Gong, of Alpha Lab, Qihoo 360 Technology Co. Ltd. One of the exploits meant that Guang got the biggest bug bounty award from Google so far this year ($201,337). Since 2015 Google has paid out a total of $4.5m in bug bounties to researchers with $1.5m of this sum awarded in 2019.






